Illex coindetii
Michael Vecchione and Richard E. YoungIntroduction
This species has the broadest distribution within the genus, being found found on both sides of the North Atlantic. It is common in the eastern North Atlantic and Mediterranean and it the target of commercial fisheries there.
Characteristics
- Arms
- Hectocotylus (either left or right arm IV)
 Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window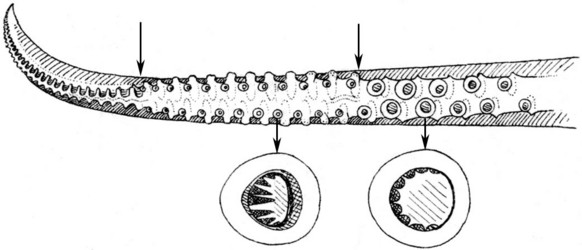
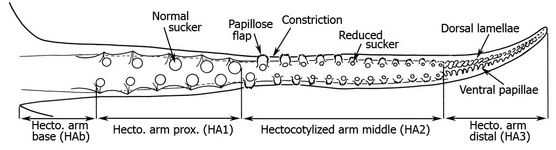
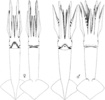
Figure. Oral view of the hectocotylus and selected suckers of I. coindetii. Upper arrows mark the divisions between the three divisions of the hectocotylus. Drawing modified from Naef (1921-23).
- Hectocotylus shorter than or equal to its opposite arm in length, always equal in thickness.
- Distal portion (HA3) about 25% (17-30%) of total arm length; dorsal series starts with 1-2 proximal conical knobs followed by truncate lamellae; ventral series starts with 1-2 conical knobs followed by digitate papillae.
- Basal portion (HAb) about 13% (10-14%) of total arm length.
- Proximal portion (HA1) with 5 - 7 pairs of normal suckers increasing in size distally.
- Middle portion (HA2) with suckers about 1/2 diameter of proximal suckers; sucker series widely separated; conspicuous constriction between HA1 and HA2.
- Trabeculae distal to largest normal suckers (HA1) modified as fringed lobes.
- Hectocotylus shorter than or equal to its opposite arm in length, always equal in thickness.
- Hectocotylus (either left or right arm IV)
- Tentacles
- Largest distal medial manal sucker-rings notched in distal half or all around.
- Largest distal medial manal sucker-rings notched in distal half or all around.
- Head
- Head-width index high, 19-26.
- Beaks: Lower beak with jaw edge long, wings long and wide, rostral width narrow, lateral wall short. Upper beak with hood long, shoulder smooth, rostrum long, wing short, jaw angle with small notch but no tooth, lateral wll short, crest curved .
- Head-width index high, 19-26.
- Fins
- Fin angle > 50°.
- Fin angle > 50°.
- Reproductive structures
- Spermatophore: "Spermatophore cone at oral end of cement body, low, rounded triangle lens-shaped or diamond-shaped in outline; oral tube broad; aboral neck of cement body very short, broad, indistinct." (Roper, et al., 1998).
Distribution
Figure. Distribution chart of all four species of Illex; modified from Roper et al. (1998).Geographícal Distribution : Eastern Atlantic: 15°S to 60°N, Mediterranean and Black Sea. Western Atlantic: Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico and southeast Florida; 1O°N to 27°N.

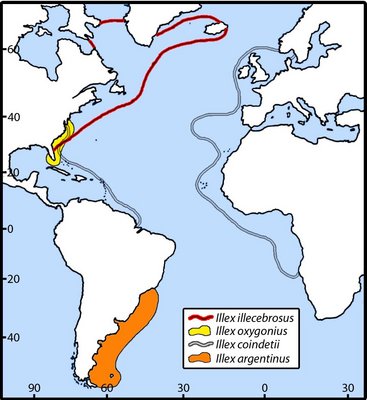
Figure. Distribution chart of all four species of Illex; modified from Roper et al. (1998).
The squids are known to carry out diel vertical movements: they are associated with the bottom (usually muddy to silty grounds) during the day and disperse into the water column at night. They also migrate seasonally between deeper waters in winter and shallower waters in the summer.
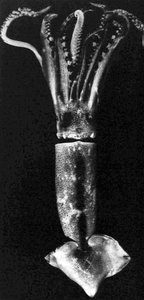
Title Illustrations

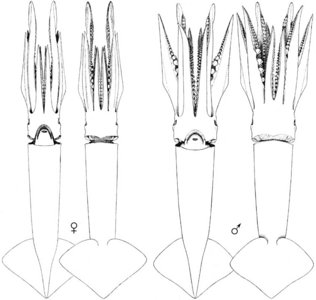
| Scientific Name | Illex coindetii |
|---|---|
| Location | Mediterranean Sea |
| Reference | Modified from: Naef, A. 1921-1923. Die Cephalopoden. Fauna e Flora del Golfo di Napoli, Monographie 35, Vol I, Parts I and II, Systematik, pp 1-863. |
| Sex | Immature female, mature male |
| View | Dorsal, ventral |
| Size | 95 mm ML (female), 150 mm ML |
| Scientific Name | Illex coindetii |
|---|---|
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Sex | Male |
| Life Cycle Stage | mature |
| Size | 132 mm ML |
| Collection | USNM |
| Type | Neotype |
| Image Use |
 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
©

|
About This Page

National Museum of Natural History, Washington, D. C. , USA

University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI, USA
Page copyright © 2018 and
 Page: Tree of Life
Illex coindetii .
Authored by
Michael Vecchione and Richard E. Young.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Illex coindetii .
Authored by
Michael Vecchione and Richard E. Young.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- First online 13 January 2011
- Content changed 13 January 2011
Citing this page:
Vecchione, Michael and Richard E. Young. 2011. Illex coindetii . Version 13 January 2011 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Illex_coindetii/77444/2011.01.13 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/






 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site